Mudanças entre as edições de "Request Resolution in Adobe AEM"
| Linha 3: | Linha 3: | ||
The process looks like this: | The process looks like this: | ||
| − | a) URL Decomposition | + | a) After the URL Decomposition process, the following URL properties are extracted: |
| + | Protocol | ||
| + | Host | ||
| + | Path | ||
| + | Selector(s) | ||
| + | Extension | ||
| + | Suffix | ||
| + | Param(s) | ||
b) The `'''path'''` component of the URL is matched against a node in `'''content'''` folder | b) The `'''path'''` component of the URL is matched against a node in `'''content'''` folder | ||
Edição das 11h05min de 23 de maio de 2018
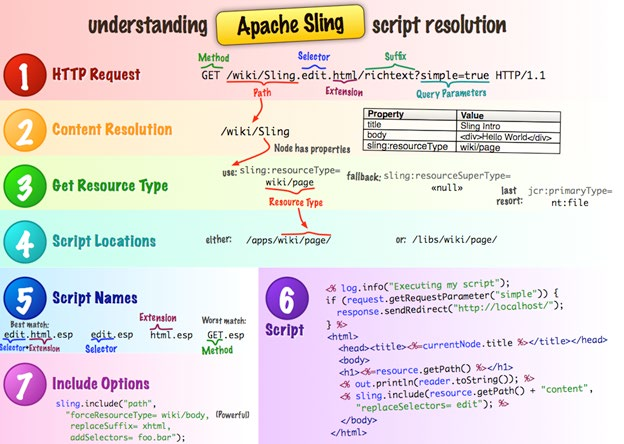
Before trying to understand request resolution, take a look at URL decomposition to see how the URL is decomposed.
The process looks like this:
a) After the URL Decomposition process, the following URL properties are extracted:
Protocol Host Path Selector(s) Extension Suffix Param(s)
b) The `path` component of the URL is matched against a node in `content` folder
c) If the node is found, it uses one of the following properties to try to locate the resource:
`sling:resourceType` `sling:resourceSuperType` `jcr:primaryType`
d) Using the value of one of the above properties, it tries to locate this resource under one of these folders:
`apps` `libs`
e) When it find the correct folder, it chooses a node with the best match based on some of the URL properties:
`Selector` `Extension` `Method`
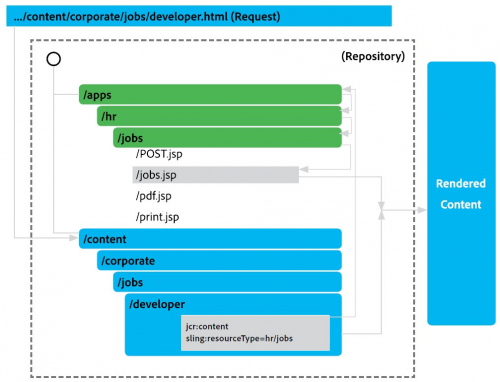
Request Example
http://myhost/content/corporate/jobs/developer.html
Notice how the resolutions starts at `content` folder, then uses a file in `apps` folder by `sling:resourceType` reference: